Understanding the differences between ethnicity and race is crucial in today's globalized world. These terms are often used interchangeably, but they carry distinct meanings that shape our identities and societal interactions. By exploring their nuances, we can foster greater cultural awareness and inclusivity.
As societies become increasingly diverse, the importance of distinguishing between ethnicity and race becomes more pronounced. Both concepts influence how individuals perceive themselves and are perceived by others, affecting everything from personal relationships to public policies.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of the differences between ethnicity and race. We will delve into their definitions, historical contexts, cultural implications, and the role they play in shaping modern societies. By the end, readers will have a clearer understanding of these complex concepts.
Read also:Jennifer Kish And David Goggins The Inspiring Journey Of A Power Couple
Table of Contents
- Defining the Terms: Ethnicity and Race
- Historical Context of Ethnicity and Race
- Cultural Identity and Ethnicity
- Biological Aspects of Race
- Social Implications of Ethnicity and Race
- Legal Perspectives on Ethnicity and Race
- Global Differences in Understanding Ethnicity and Race
- Overlapping Concepts: Ethnicity and Race
- Common Misconceptions About Ethnicity and Race
- Conclusion: Embracing Diversity
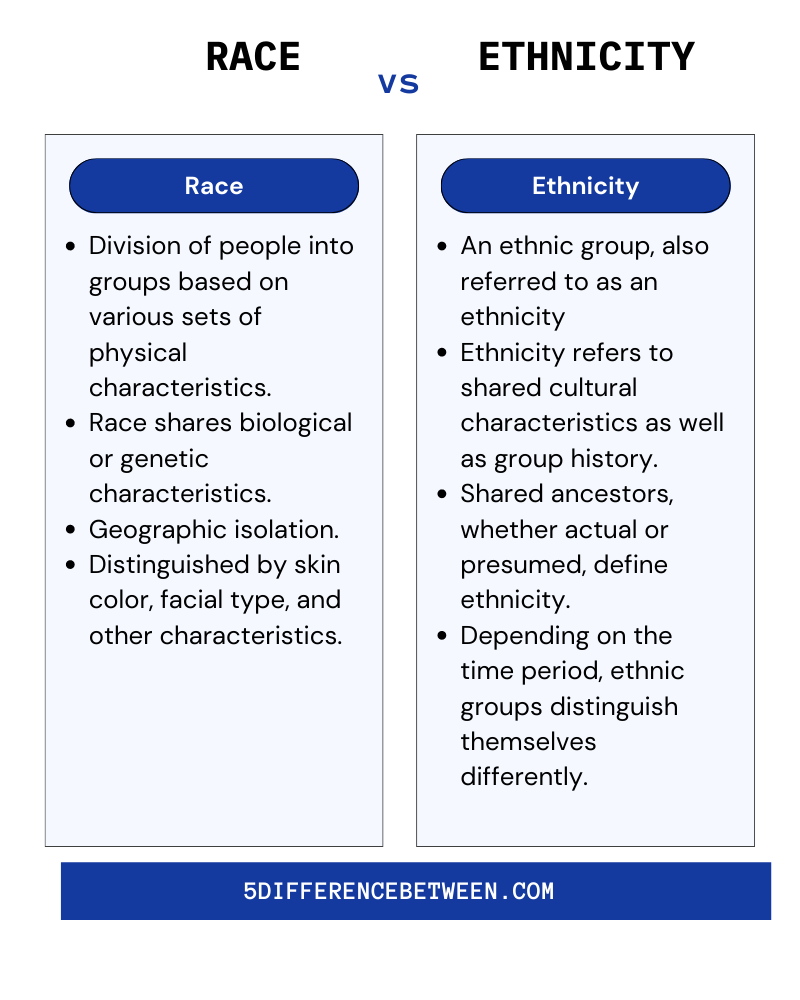
Defining the Terms: Ethnicity and Race
Before diving into the differences, it is essential to define ethnicity and race clearly. Ethnicity refers to a shared cultural heritage, including language, traditions, religion, and ancestry. It is a social construct that reflects a group's identity and shared practices.
Race, on the other hand, is often linked to physical characteristics such as skin color, facial features, and hair texture. While race is also a social construct, it has been historically used to categorize people based on perceived biological differences.
Understanding these definitions is the first step in recognizing the distinctions between ethnicity and race. Both concepts influence individual and group identities but operate in different ways.
Key Characteristics of Ethnicity
- Based on cultural and social factors
- Can be voluntarily adopted or changed
- Focuses on shared traditions and practices
Key Characteristics of Race
- Linked to physical attributes
- Often imposed by societal structures
- Historically used for classification and discrimination
Historical Context of Ethnicity and Race
The concepts of ethnicity and race have evolved over centuries, shaped by historical events and societal changes. During colonial times, race was used as a tool for categorization and control, often leading to systemic discrimination and inequality.
Ethnicity, meanwhile, has been a source of unity and identity for communities. It has allowed groups to preserve their unique cultural heritage despite external pressures. However, ethnic identities can also lead to conflicts when they intersect with political or economic interests.
By examining the historical context, we gain insights into how these concepts have been used and misused throughout history.
Read also:Hailey Bieber Engagement Ring Details A Comprehensive Guide To Love Luxury And Style
The Role of Colonialism
Colonialism played a significant role in shaping modern understandings of race. European powers categorized colonized populations based on perceived racial hierarchies, justifying exploitation and oppression.
Post-Colonial Shifts
After decolonization, many societies began redefining their ethnic and racial identities. This period saw a rise in movements advocating for cultural preservation and racial equality.
Cultural Identity and Ethnicity
Cultural identity is closely tied to ethnicity. It encompasses the values, beliefs, and practices that define a group's way of life. Ethnic identity provides individuals with a sense of belonging and connection to their heritage.
For example, a person of Irish descent may celebrate St. Patrick's Day, speak Gaelic, or practice Catholicism as part of their ethnic identity. These cultural markers help differentiate one ethnic group from another.
While cultural identity is fluid and can adapt to new environments, it remains a powerful force in shaping individual and group identities.
Challenges in Preserving Ethnic Identity
- Globalization and cultural assimilation
- Migration and integration into new societies
- Loss of traditional practices and languages
Biological Aspects of Race
Despite popular belief, race lacks a solid biological basis. Scientific studies have shown that genetic variation within so-called racial groups is greater than the variation between them. This challenges the notion of race as a fixed biological category.
However, the perception of race continues to influence societal interactions. Racial categories have been ingrained in social systems, affecting everything from education to healthcare.
Understanding the biological aspects of race helps dispel myths and promotes a more nuanced view of human diversity.
Genetic Diversity and Race
Research indicates that genetic diversity exists across all populations, undermining the idea of distinct racial groups. This scientific evidence supports the argument that race is primarily a social construct.
Social Implications of Ethnicity and Race
Ethnicity and race have profound social implications that affect individuals and communities. They influence how people are treated, the opportunities they receive, and the challenges they face.
Racial discrimination remains a significant issue in many societies, manifesting in various forms such as prejudice, stereotyping, and systemic inequality. Ethnic tensions can also lead to conflicts, especially in multicultural settings.
Promoting awareness and understanding of these issues is vital for building inclusive and equitable societies.
Addressing Racial Inequality
- Implementing anti-discrimination policies
- Promoting diversity and inclusion initiatives
- Encouraging intercultural dialogue and understanding
Legal Perspectives on Ethnicity and Race
Legal frameworks play a crucial role in addressing issues related to ethnicity and race. Laws and regulations aim to protect individuals from discrimination and promote equality.
In many countries, race is recognized as a protected characteristic under anti-discrimination laws. Ethnicity, while less commonly addressed, is also protected in some jurisdictions, particularly when it intersects with race.
However, enforcing these laws can be challenging, especially when discrimination is subtle or systemic.
International Human Rights Standards
International bodies such as the United Nations have established standards for combating racial discrimination. These frameworks provide guidance for national governments in addressing issues of ethnicity and race.
Global Differences in Understanding Ethnicity and Race
Perceptions of ethnicity and race vary significantly across the globe. Cultural, historical, and political factors influence how these concepts are understood and applied in different regions.
For instance, in some countries, ethnicity is the primary basis for identity, while in others, race plays a more significant role. These differences highlight the complexity of global diversity.
Recognizing these variations is essential for fostering cross-cultural understanding and cooperation.
Regional Perspectives
- African contexts: Ethnicity often dominates identity politics
- Asian contexts: Race and ethnicity intersect in unique ways
- European contexts: Historical legacies shape contemporary views
Overlapping Concepts: Ethnicity and Race
While ethnicity and race are distinct concepts, they often overlap in practice. Many individuals identify with both ethnic and racial categories, creating complex identity dynamics.
This overlap can lead to confusion or misunderstanding, especially when discussing issues of diversity and inclusion. Clarifying the distinctions while acknowledging the intersections is key to effective communication.
For example, a person may identify as Black (race) and Nigerian (ethnicity), reflecting both their physical characteristics and cultural heritage.
Intersectionality in Identity
Intersectionality theory highlights how multiple aspects of identity, including ethnicity and race, intersect to shape individual experiences. This framework helps explain the unique challenges faced by individuals with overlapping identities.
Common Misconceptions About Ethnicity and Race
Misunderstandings about ethnicity and race persist, perpetuating stereotypes and misinformation. Some common misconceptions include:
- Believing race is a biologically fixed category
- Assuming all members of an ethnic group share the same beliefs
- Thinking ethnicity and race are interchangeable terms
Addressing these misconceptions requires education and open dialogue. Encouraging critical thinking and empathy can help dismantle harmful stereotypes.
Conclusion: Embracing Diversity
In conclusion, understanding the differences between ethnicity and race is essential for promoting inclusivity and equality. While both concepts influence individual and group identities, they operate in distinct ways. By recognizing their nuances, we can foster greater cultural awareness and respect.
We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Your input can contribute to a broader understanding of these complex issues. Additionally, explore other articles on our site to deepen your knowledge of diversity and inclusion topics.
References:
- United Nations. (2022). International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination.
- American Anthropological Association. (1998). Statement on Race.
- Pew Research Center. (2021). Racial and Ethnic Identity in the U.S.
- Was Damon Imani On The View Exploring The Connection Between The Renowned Musician And The Talk Show