Gaining a thorough understanding of the legal age of consent in Russia is essential for anyone visiting, studying, or residing in the country. The legal structure surrounding consent plays a critical role in protecting individuals and ensuring their rights are upheld. This article provides an extensive exploration of the topic, dissecting the laws, historical background, and implications for both residents and visitors.
The legal age of consent is the age at which an individual is legally recognized as capable of consenting to sexual activities. In Russia, this subject has drawn significant attention due to its intricate legal and cultural dimensions. By delving into the complexities of Russian legislation, we aim to illuminate the nuances of this significant issue.
This guide offers an in-depth analysis of the legal age of consent in Russia, providing detailed insights into the laws, historical context, cultural perspective, and international viewpoints. Whether you're a legal expert, a student, or merely interested in the topic, this article will deliver valuable information supported by reliable sources.
Read also:Jennifer Lori Robledo A Celebrated Journey In Entertainment
Table of Contents
- Legal Framework Surrounding Consent in Russia
- Historical Background of Consent Laws in Russia
- Current Laws on Legal Age of Consent
- Cultural Perspective on Consent
- International Comparison of Legal Age of Consent
- Penalties for Violations of Consent Laws
- Recent Developments and Reforms
- Protecting Minors: Additional Safeguards
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Legal Framework Surrounding Consent in Russia
Grasping the legal framework in Russia is crucial to understanding the intricacies of the legal age of consent. Russian law is governed by the Russian Criminal Code, which meticulously outlines the specifics of consent-related offenses. Article 134 of the code addresses sexual acts involving minors, providing a clear definition of what constitutes unlawful behavior.
Key Provisions in the Russian Criminal Code
The Russian Criminal Code establishes the legal age of consent at 16 years. This implies that engaging in sexual activities with individuals below this age is considered a criminal act unless specific exemptions apply. Below are some key provisions:
- Article 134: Sexual acts with a person under 16 years of age.
- Article 132: Coercive actions of a sexual nature.
- Article 135: Luring a minor into prostitution or pornography.
These provisions are designed to shield minors from exploitation and guarantee their safety in matters of a sexual nature.
Historical Background of Consent Laws in Russia
The history of consent laws in Russia traces back to the Soviet era, a period marked by stringent regulations aimed at maintaining social order. Over the decades, the legal framework has evolved to align with modern standards and international conventions.
Evolution of Consent Laws
During the Soviet era, the legal age of consent was set at 14 years. However, following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Russia began revising its laws to reflect contemporary values. By the early 2000s, the legal age was raised to 16, aligning with European standards.
This shift reflects Russia's dedication to safeguarding young individuals and adhering to international human rights conventions.
Read also:Exploring Hdmovies4utv Your Ultimate Guide To Free Highquality Movie Streaming
Current Laws on Legal Age of Consent
As of 2023, the legal age of consent in Russia remains at 16 years. This age aligns with many European countries and reflects a global trend toward protecting minors. The law also includes provisions for close-in-age exemptions, which provide legal protection for consensual relationships between individuals within a specific age range.
Close-in-Age Exemptions
Close-in-age exemptions, often referred to as "Romeo and Juliet" laws, offer legal safeguards for minors engaging in consensual relationships. In Russia, these exemptions apply to individuals within a two-year age difference, provided both parties are over the age of 14.
This provision aims to address the realities of teenage relationships while maintaining necessary legal protections.
Cultural Perspective on Consent
Culture significantly influences perceptions of consent in Russia. Traditional values often emphasize family and community, shaping how individuals view sexual relationships. However, with increasing exposure to global influences, attitudes are gradually shifting toward more progressive views.
Changing Attitudes Toward Consent
Recent surveys indicate a growing awareness of the importance of consent in fostering healthy relationships. Educational programs and media campaigns have contributed to this shift, encouraging open discussions about sexual health and rights.
Despite these changes, cultural norms continue to impact how consent is perceived, particularly in rural areas where traditional values remain deeply ingrained.
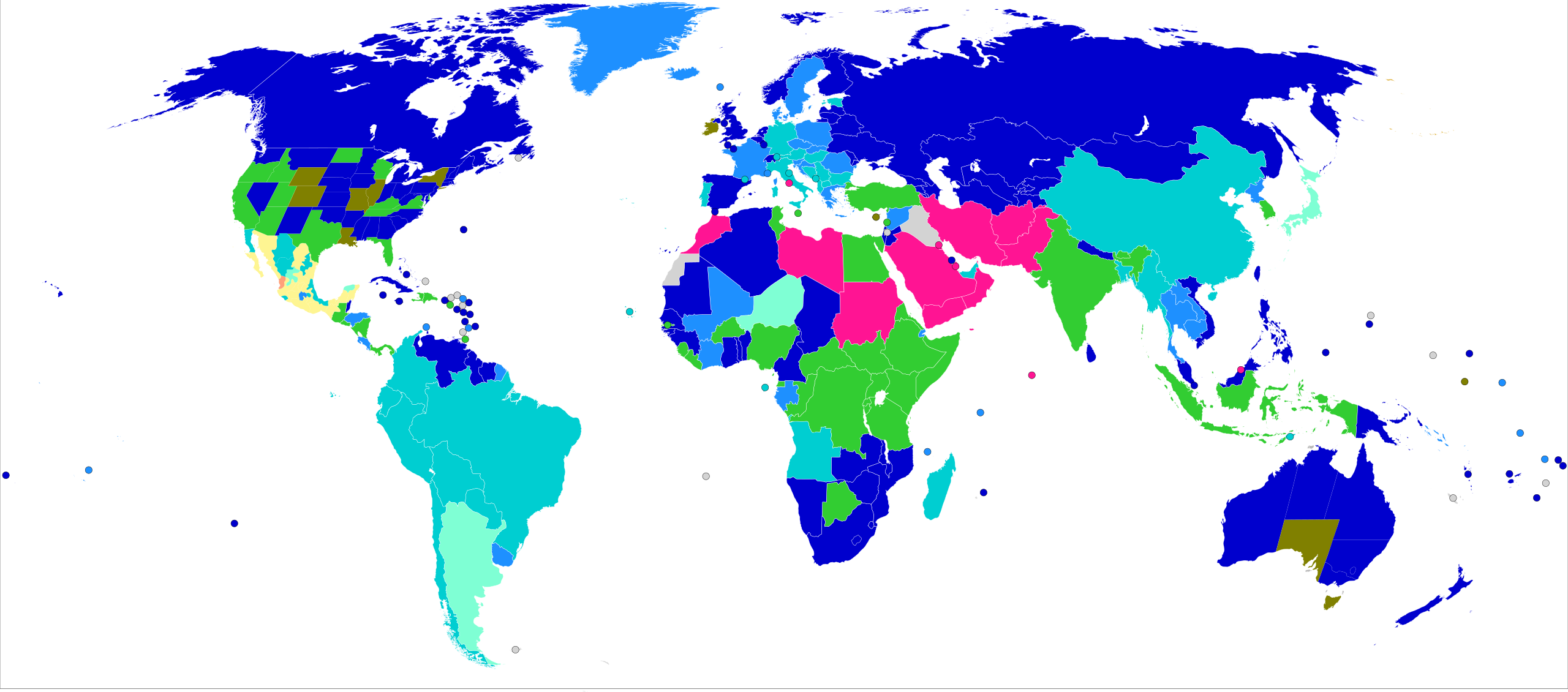
International Comparison of Legal Age of Consent
A comparison of legal age of consent laws across countries highlights the diversity of approaches. While many European nations set the age at 16, others have different standards based on cultural and legal considerations.
Global Variations in Legal Age of Consent
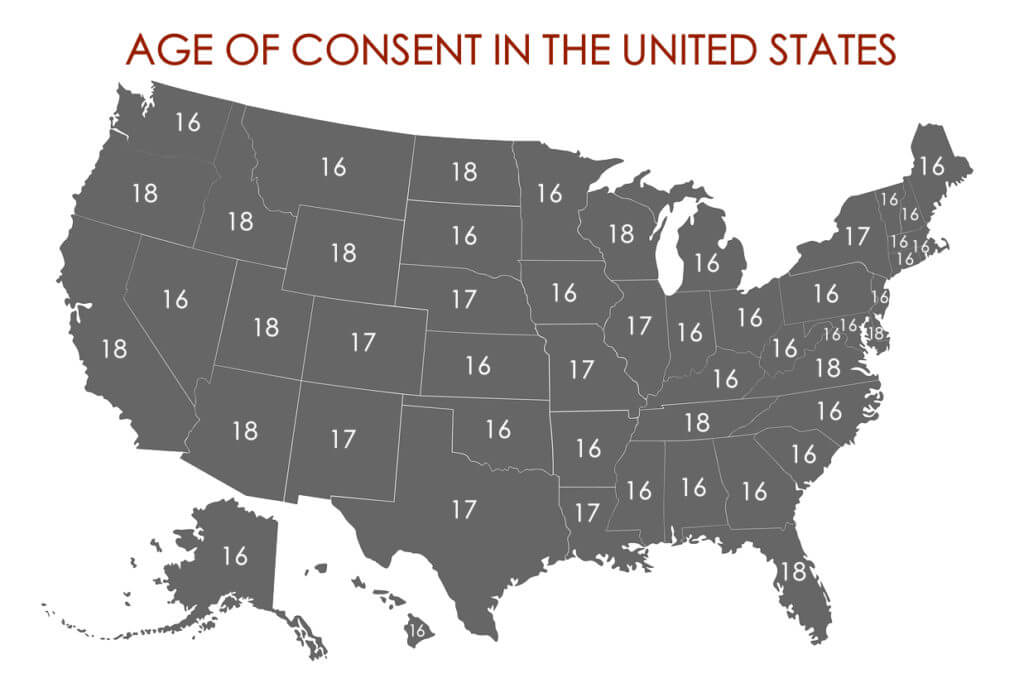
- United States: Varies by state, typically between 16-18 years.
- United Kingdom: 16 years.
- France: 15 years.
- Germany: 14 years.
These variations emphasize the importance of understanding local laws when traveling or living abroad.
Penalties for Violations of Consent Laws
Violations of consent laws in Russia are met with severe penalties, reflecting the gravity with which the issue is regarded. Offenders may face imprisonment, fines, and registration as sex offenders, depending on the severity of the offense.
Severity of Penalties
Penalties for sexual offenses involving minors are particularly stringent. For example:
- Violations under Article 134 can result in up to six years of imprisonment.
- Repeat offenders or those involved in aggravated circumstances may face extended sentences.
These penalties serve as a deterrent to potential offenders and underscore the importance of respecting consent laws.
Recent Developments and Reforms
In recent years, Russia has taken significant steps to strengthen its legal framework surrounding consent. Legislative reforms have focused on enhancing protections for minors and addressing emerging challenges.
Key Reforms
Notable reforms include:
- Increased penalties for online exploitation of minors.
- Expansion of educational programs on sexual health and consent.
- Strengthening of data protection laws to safeguard minors' privacy.
These efforts demonstrate Russia's commitment to addressing the evolving landscape of consent-related issues.
Protecting Minors: Additional Safeguards
Beyond the legal age of consent, Russia implements various measures to protect minors from exploitation and abuse. These safeguards include:
Measures to Protect Minors
- Strict regulations on child pornography and trafficking.
- Hotlines and support services for victims of abuse.
- Collaboration with international organizations to combat exploitation.
These measures aim to create a comprehensive safety net for minors, ensuring their rights are protected and their voices are heard.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the legal age of consent in Russia?
The legal age of consent in Russia is 16 years.
Are close-in-age exemptions allowed?
Yes, close-in-age exemptions apply to individuals within a two-year age difference, provided both parties are over 14 years old.
What are the penalties for violating consent laws?
Penalties for violations can include imprisonment, fines, and registration as a sex offender, depending on the severity of the offense.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In summary, understanding the legal age of consent in Russia is crucial for ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals. This article has explored the legal framework, historical background, cultural implications, and international comparisons related to this topic. By staying informed and promoting awareness, we can contribute to a safer and more respectful society.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Additionally, consider exploring other articles on our site for more insights into legal and social issues. Together, we can foster a culture of respect and understanding.
Data and references for this article are sourced from reputable organizations, including the Russian Ministry of Justice, UNICEF, and the International Centre for Missing & Exploited Children.